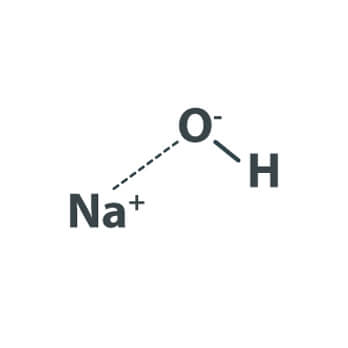
Caustic soda Flakes is manufactured from Caustic Soda Lye produced by Membrane Cell Technology. It is an inorganic compound with formula NaOH. It is highly soluble in water readily absorbs moisture and carbon dioxide from the air.
Applications: Soaps and detergents, Sodium Salts, Cosmetics
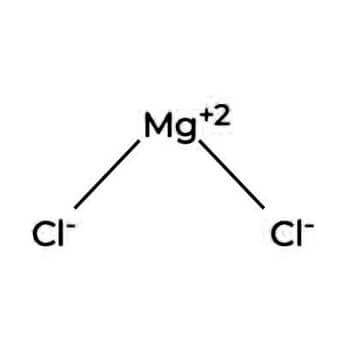
Magnesium chloride is the name for the chemical compound with the formula MgCl2 and its various hydrates MgCl2(H2O)x. These salts are typical ionic halides, being highly soluble in water. They hydrated magnesium chloride can be extracted from brine or sea water.
Applications: Feed, Textiles, Fertilizer, Mineral Supplement, paper and fireproofing agents.
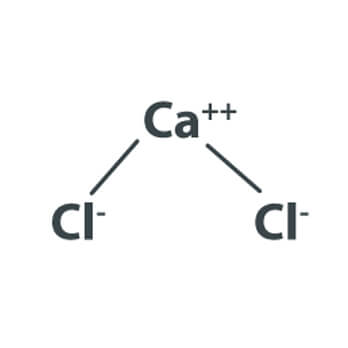
Calcium Chloride is an inorganic compound, a salt with the chemical formula CaCl2. It is a colorless c rystalline solid at room temperature, Highly Soluble in water. It is used for de-icing, dust control and as a desiccant
Applications:Medicine, Food, Road Surfacing, Water Treatment.
Ethyl acetate is used primarily as a solvent and diluent, being favoured because of its low cost, low toxicity, and agreeable odor. For example, it is commonly used to clean circuit boards and in some nail varnish removers (acetone is also used). Coffee beans and tea leaves are decaffeinated with this solvent. It is also used in paints as a activator or hardener. Ethyl acetate is present in confectionery, perfumes, and fruits. In perfumes, it evaporates quickly, leaving only the scent of the perfume on the skin.
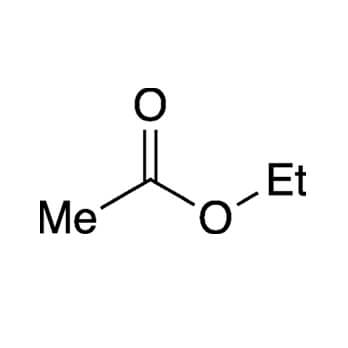
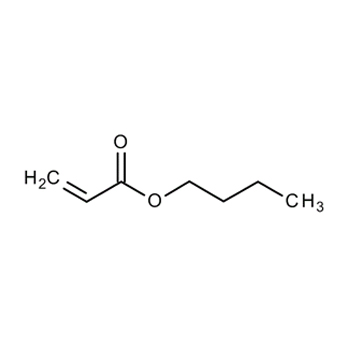
Butyl acrylate is a colourless transparent liquid. It is used to manufacture homopolymers and copolymers. Copolymers of butyl acrylate can be produced with acrylic acid and its salts, amides and esters, and with methacrylate’s, acrylonitrile, maleic acid esters, vinyl acetate, vinyl chloride, vinylidene chloride, styrene, butadiene, unsaturated polyesters and drying oils, etc. Butyl acrylate can also be used as raw material for chemical synthesis, as it undergoes addition reactions with variety of organic and inorganic compounds
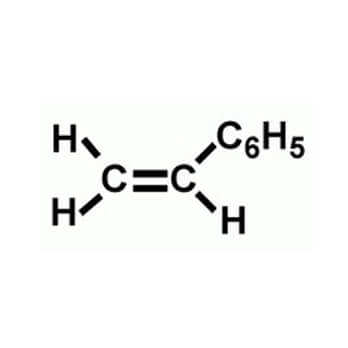
Styrene is a clear, colourless aromatic liquid that comes from petroleum and natural gas. Styrene – based polymers are used to make products we use every day such as appliances and electronics, automotive components, flooring, insulation, medical devices, packaging, paper coatings, toys and consumer goods, and tires.
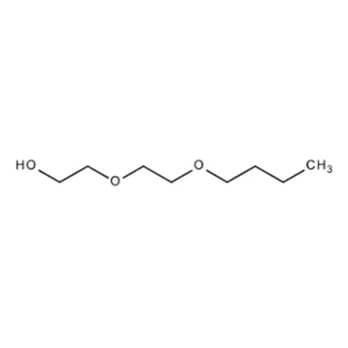
A versatile glycol ether used extensively in the surface coatings and chemi cal manufacturing industries. It can be used in water based architectural and industrial coatings a s a latex coalescent, as a cosolvent in industrial cleaners, household surface cleaners and disinfectants, as well as resins and dyes in water-based printing inks.
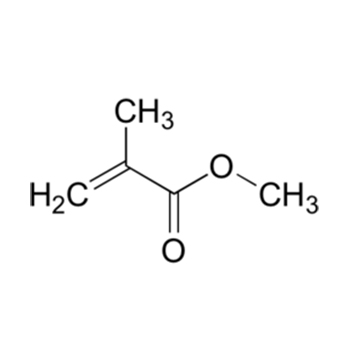
The principal application, consuming approximately 75% of the MMA, is the manufacture of polymethyl methacrylate acrylic plastics (PMMA). Methyl methacrylate is also used for the production of the co -polymer methyl methacrylate – butadiene-styrene (MBS), used as a modified for PVC. Another application is as cement used in total hip replacements as well as total knee replacements. Used a s the “grout” by orthopaedic surgeons to make the bone inserts fix into bone, it greatly reduces post -operative pain from the insertions but has a finite lifespan. Typically, the lifespan of methyl methacrylate as bone cement is 20 years before revision surgery is required. Cemented implants are usually only done in elderly populations that require more immediate short – term replacements. In younger populations, cementless implants are used because their lifespan is considerably longer. Also used infracture repair in small exotic animal species using internal fixation.
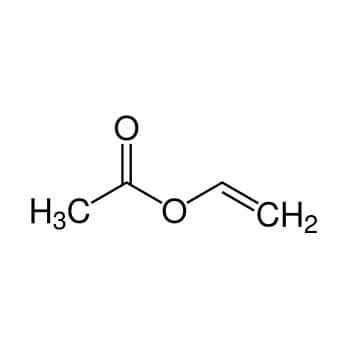
Vinyl acetate monomer (VAM) is a key intermediate used in the making of a number of polymers and resins for adhesives, coatings, paints, films, textiles and other end -products. VAM is consumed in the manufacture of ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and vinyl acetate ethylene (VAE). EVA, which has less than 50% vinyl acetate in content, is mainly used for films and wire and cable insulation. VAE, which contains more than 50% vinyl acetate, is primarily used as cement additives, paints and adhesives.
Butyl di glycol (also known as BDG, butyl dienitol, diethylene glycol mono butyl ether, 2(- 2butoxyethoxy) ethanol and butoxy diethylene glycol) is a colourless, clear organic compound with a faint characteristic odour that has the formula C8H18O3. It is soluble in water and miscible with many common solvents, and also has low volatility and a high boiling point. These are the factors that make butyl di glycol most useful in the paint industry
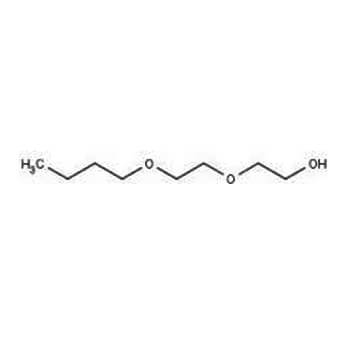
Glycol ethers, with both an ether and alcohol functional group in the same molecule, are one of the most versatile classes of organic solvents. The product line consists of more than 10 distinct chemicals.
Butyl glycol is a clear, colourless oily liquid with a high boiling point, low volatility and a mild fruity odour. Like other glycol ethers, it has a bi -functional nature, containing both an ether and an alcohol group in the same molecule. It is fully miscible with water and a wide range of organic solvents. This excellent miscibility makes it a versatile solvent and coupling agent which offers excellent performance features in a wide range of applications.
Mixed xylenes are produced by several methods but petroleum is by far the major source. para – Xylene is the most widely
used of the three xylene isomers. The major application for para -xylene is, by far, the production of purified terephthalic acid (PTA), which itself is used almost exclusively for the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) polymer for the manufacture of polyester fibres, PET solid-state resins, and PET film. The past 15 years have seen substantial investment in mixed xylenes capacity, primarily for use in para -xylene. These investments have been located mainly in Northeast Asia, which has a well -developed, integrated polye ster industry as well as access to raw materials. Asian polyester producers have moved to back -integrate their business
into purified terephthalic acid, para -xylene, and mixed xylenes to improve their cost -competitiveness.
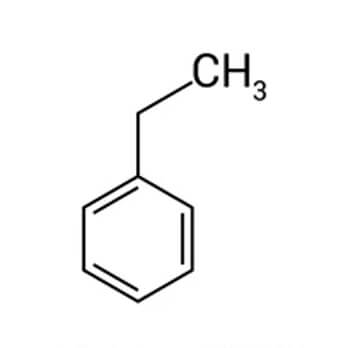
Toluene is a common solvent, e.g. for paints, paint thinners, silicone sealants, many chemical reactants, rubber, printing ink, adhesives (glues), lacquers, leather tanners, and disinfectants. In the laboratory, toluene is used as a solvent for carbon nanomaterials, including nanotubes and
fullerenes, and it can also be used as a fullerene indicator. The colour of the toluene solution of C60 is bright purple. Toluene is used as a cement for fine polystyrene kits (by dissolving and then fusing surfaces) as it can be applied very precisely by brush and contains none of the bulk of an adhesive.
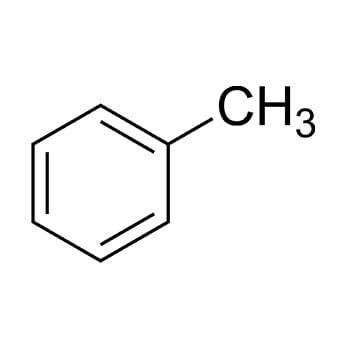
In the Chevron Phillips slurry process for making high -density polyethylene, isobutane is used as a diluent. As the slurred polyethylene is removed, isobutane is “flashed” off, and condensed, and recycled back into the loop reactor for this purpose.
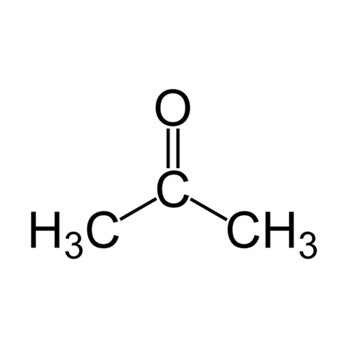
Acetone is a good solvent for many plasticsand some synthetic fibers. It is used for thinning polyester resin, cleaning tools used with it, and dissolving two -part epoxies and superglue before they harden. It is used as one of the volatile components of some paints and varnishes. As a heavy – duty degreaser, it is useful in the preparation of metal prior to painting or soldering, and to remove rosin flux after soldering, which hel ps to prevent the rusty bolt effect.
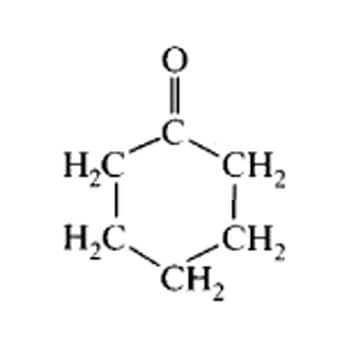
The great majority of cyclohexanone is consumed in the production of precursors to Nylon 6,6 and Nylon 6. About half of the world’s supply is converted to adipic acid, one of two precursors for nylon 6,6. For this application, the KA oil (see above) is oxidized with nitric acid. The other half of the cyclohexanone supply is converted to cyclohexanone oxime. In the presence of sulfuric acid catalyst, the oxime rearranges to caprolactam, a precursor to nyl on 6.
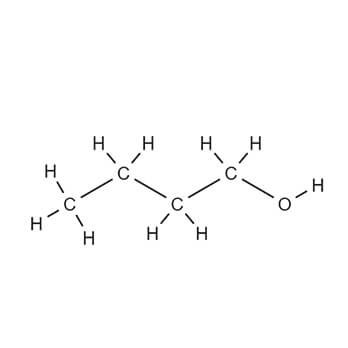
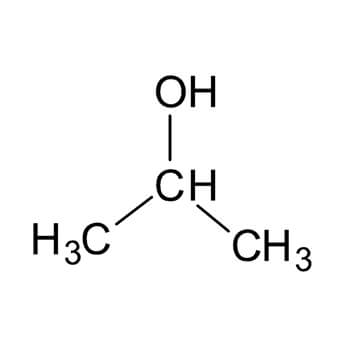
Isopropyl alcohol dissolves a wide range of non -polar compounds. It also evaporates quickly, leaves nearly zero oil traces,
compared to ethanol, and is relatively non – toxic, compared to alternative solvents. Thus, it is use d widely as a solvent and as a cleaning fluid, especially for dissolving oils. Together with ethanol, n -butanol, and methanol, it belongs to the group of alcohol solvents, about 6.4 million tonnes of which were used worldwide in
2011.
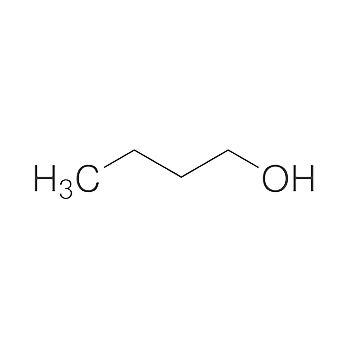
The production or, in some cases, use of the following substances may result in exposure to n – butanol: artificial leather, butyl esters, rubber cement, dyes, fruit essences, lacquers, motion picture, and photographic films, raincoats, perfumes, pyroxylin plastics, rayon, safety glass, shellac varnish, and waterproofed cloth
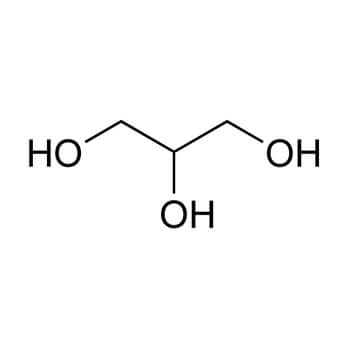
The most recent advances in the use of glycerol and glycerol derivatives as solvents are reviewed. There are an increasing number of examples of the use of glycerol itself as a reaction medium, solvent–reagent or a dispersive medium for a large variety of applications. In the case of glycerol derivatives, new synthetic methods, physico-chemical properties and application examples as solvents are revised. Recent studies in the field of solvent classification, as well as solvent substitution issues, in connection with glycerolderivatives are also discussed in this review.
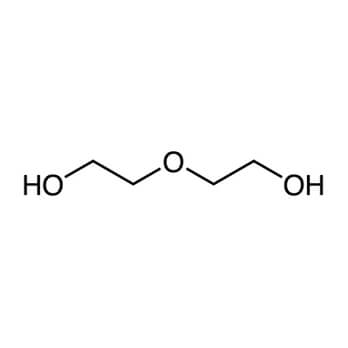
Diethylene glycol (also known as DEG, 2,2- oxydiethanol and glycol ether ether glycol) is a clear, colourless, odourless liquid with the formula C4H10O3. It is soluble both in water and in many organic compounds and has hygroscopic properties which makes it a useful industrial chemical.
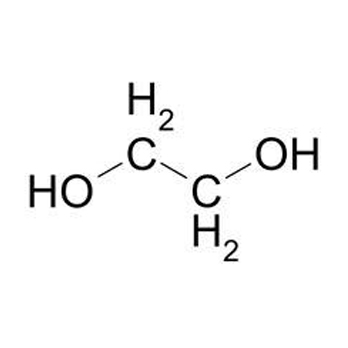
Mono Ethylene Glycol (also known as MEG) is a clear, colourless, virtually odourless, and slightly viscous liquid. It is miscible with water, al cohols, and many organic compounds, and has the formula C2H6O2. It is the most important of the commercially available ethylene glycols as it has many industrial applications.
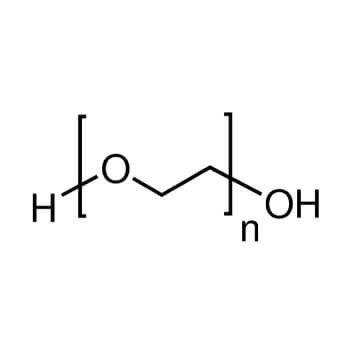
PEG has a vast number of applications in the medical industry, and the list continues to grow. Due to its non-toxicity and high solubility , it lends it self to many pharmaceutical and bio medical applications. To begin with, possibly the most common application of PEG in the medical industry is its use in laxatives. Because PEG can apply osmotic pressure, it can draw water into the waste matter, providing a laxative effect.
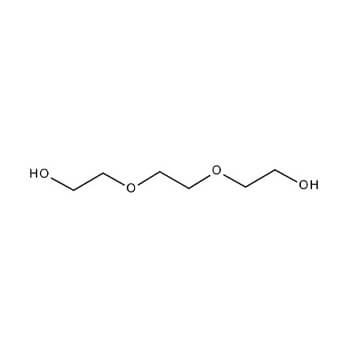
TEG is used by the oil and gas industry to “dehydrate” natural gas. It may also be used to dehydrate other gases, including CO2, H2S, and other oxygenated gases. It is necessary to dry natural gas to a certain point, as humidity in natural gas can cause pipelines to freeze, and create other problems for end users of the natural gas. Triethylene glycol is placed into contact with natural gas, and strips the water out of the gas. Triethylene glycol is heated to a high temperature and put through a condensing system, which removes the water as waste and reclaims the TEG for continuous reuse
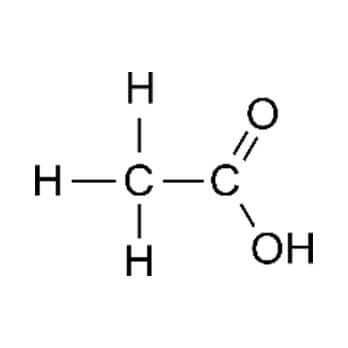
Acetic acid has 349 kcal per 100 g. Vinegar is typically no less than 4% acetic acid by mass. Legal limits on acetic acid content vary by jurisdiction. Vinegar is used directly as a condiment, and in the pickling of vegetables and other foods. Table vinegar tends to be more diluted (4% to 8% aceticacid), while commercialfood pickling employs solutions that are more concentrated. The proportionof acetic acid used worldwide as vinegar is not as large as commercial uses, but is by far the oldestand best-known application.
The primary use of DMF is as a solvent with low evaporation rate. DMF is used in the production of acrylic fibers and plastics. It is also used as a solvent in peptide coupling for pharmaceuticals, in the development and production of pesticides, and in the manufacture of adhesives, synthetic leathers, fibers, films, and surface coatings

Nonylphenol is used in manufacturing antioxidants, lubricating oil additives, laundry and dish detergents, emulsifiers,
and solubilizers. It can also be used to produce tris(4-nonyl-phenyl) phosphite (TNPP), which is an antioxidant used to protect polymers, such as rubber, Vinyl
polymers, polyolefins, and polystyrenics in addition to being a stabilizer in plastic food packaging. Barium and calcium salts of nonylphenol are also used as heat stabilizers for polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Nonylphenol is also often used an intermediate in the manufacture of the non-ionic surfactants nonylphenol ethoxylates, which are used in detergents, paints, pesticides, personal care products, and plastics. Nonylphenol and nonylphenol ethoxylates are only used as components of household detergents outside of Europe. Nonyl Phenol, is used in many epoxy formulations mainly in North America
The major uses of phenol, consuming two thirds of its production, involve its conversion to precursors for plastics. Condensation with acetone gives bisphenol -A, a key precursor to polycarbonates and epoxide resins. Condensation of phenol, alkylphenols,or diphenols with formaldehyde gives phenolic resins, a famous example of which is Bakelite. Partial hydrogenation of phenol gives cyclohexanone, a precursor to nylon. Non-ionic detergents are produced by alkylation of phenol to give the alkylphenols, e.g., nonylphenol, which are then subjected to ethoxylation. Phenol is also a versatile precursor to a large collection of drugs, most notably aspirin but also many herbicides and pharmaceutical drugs.
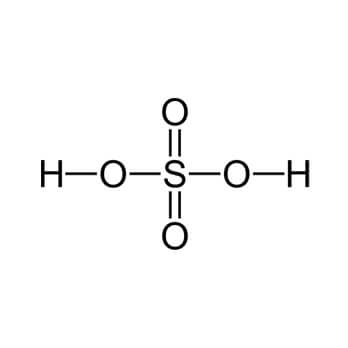
Sulfuric acid referred as universal chemical, king of chemicals due to the numerous applications for sulfuric acid as a raw material or processing agent. Sulfuric acid is the most commonly used chemical in the world and used in almost all industries like Fertilizers, Pharmaceuticals, Gasoline, Automobile batteries, Paper bleaching, Sugar bleaching, Water treatment, Sulfonation agents, Cellulose fibers
It is used for bleaching dirty clothes in the laundry, as a bleaching agent for cotton and linen in the textile industry. It is a strong oxidizing agent hence used as an oxidizer in many industries. It is used as a disinfectant which is used for disinfecting water to make potable water.
n-Butyl acetate, also known as butyl ethanoate, is an ester that is a colourless, flammable liquid at room temperature. It is found in many types of fruit, where along with other chemicals, it imparts characteristic flavours and has a sweet smell of banana or apple. It is used as a synthetic fruit flavouring in foods such as candy, ice cream, cheeses, and baked goods. Butyl acetate is often used as a high-boiling solvent of moderate polarity. It is also used as a solvent in nail polish along with ethyl acetate.
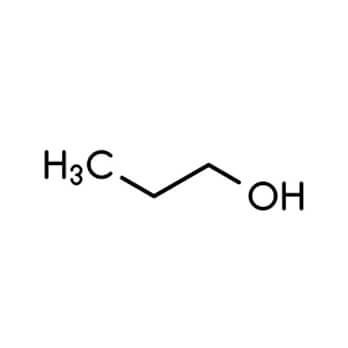
Normal propanol (also known as n-propanol, 1-propanol, Propan-1-l) is a primary alcohol with a molecular formula of CH3(CH2)2OH. It is a colourless, transparent liquid that has a typi cal sharp musty odour that is comparable with the smell of rubbing alcohol. The product is fully miscible in water and freely miscible with all common solvents such as glycols, ketones, alcohols, aldehydes, ethers and aliphatic hydrocarbons. It has a flash point of around 15° C and improves drying in coating applications.